Rare oncogenic fusion CD74-NRG1 detection in lung cancer patient

Dr. Aparna Sreevatsa
Chief Consultant Medical Oncologist, Nanjappa Hospital, Shimoga.
This case demonstrates the value of CGP in NSCLC patients who do not harbour any well-known driver mutations in genes such as EGFR, KRAS, ALK, ROS1, RET, MET, and NTRK, instead harbour other targetable alterations that would potentially benefit the patient.
Clinical Presentation
This is a case study of a 72-year-old patient, diagnosed with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) based on Histopathological analysis. The clinician referred the patient for Comprehensive Genomic Profiling (CGP) to identify the therapeutic/prognosis/diagnostic biomarkers in cancer and further plan for the potential treatment options.
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS IN THE PATIENT’S TUMOR SAMPLE
NRG1 fusions have been found in approximately 10-30% of NSCLC patients and the most prevalent NRG1 fusion partners are ATP1B1, RBPMS, SDC4, and CD74. We have identified a pathogenic CD74-NRG1 fusion in this patient’s tumor sample.
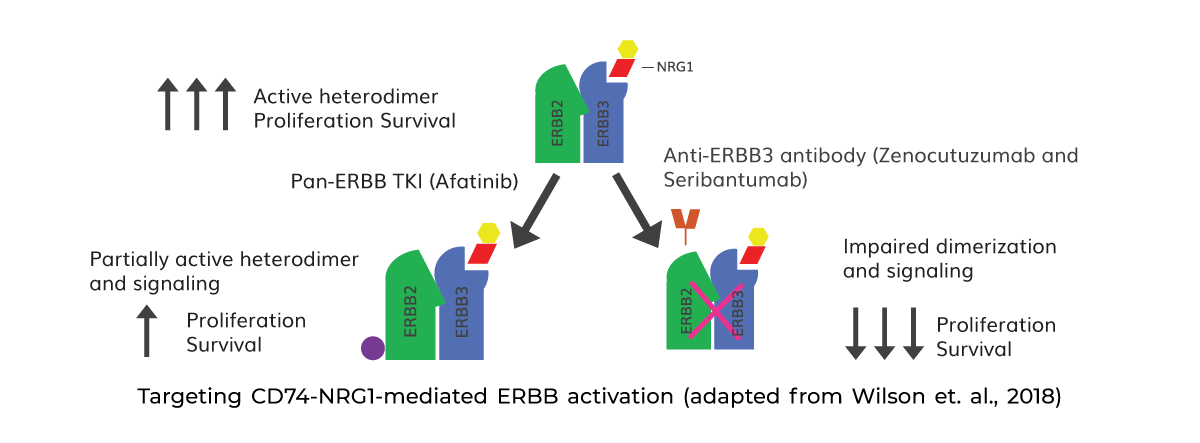
The CD74-NRG1 fusion identified in this case has a breakpoint at exon 6 of the CD74 and exon 6 of NRG1, which has been previously reported in the literature (Fernandez-Cuesta, L et al., 2014). The epidermal growth factor (EGF)‐like the domain of the fused protein binds to the tyrosine kinases of the ErbB/HER receptor family, (ERBB3, ERBB4), leading to heterodimerization. This heterodimerization leads to the activation of ErbB‐mediated downstream signaling pathways; and proliferation and survival of the cancer cells.
The CD74-NRG1 mediated ERBB activation can be targeted either with pan-ERBB TKIs (such as afatinib, left) or anti-ERBB3 antibodies (such as GSK2849330, right) as depicted in the diagram.
A pan-ERBB TKI can reduce signaling and partially inhibit ERBB2 kinase activity, which can have antitumor benefits in some patients. As per some clinically well-established studies, Afatinib, a pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor has shown significant therapeutic efficacy in NSCLC patients harboring NRG1 fusion (Duruisseaux, M et al., 2019; Cadranel, J et al., 2021). On the other side, the anti-ERBB3 antibody may result in a more powerful suppression of ERBB2–ERBB3 signaling, resulting in tumor regression. Zenocutuzumab (Zeno) and Seribantumab drugs are anti-ERBB3 antibodies that have been granted Fast Track Designation. by the FDA for the treatment of patients with metastatic solid tumours harbouring NRG1 gene fusions (NRG1+ cancers).
The key takeaway here is that CGP enabled us to find the targetable driver changes, even if they aren’t well-known biomarkers in the specific tumour type.
Authors: Ashwini P, Kritika Verma, Richa Malhotra, Sharanya J
 Kindly fill the form below to download our Liquid Biopsy Portfolio brochure :
Kindly fill the form below to download our Liquid Biopsy Portfolio brochure :